Resources Uncovered
Elementary Inquiry 2016-2017
Developed for our Final session on Thursday, May 17, 2017
CODE BC
- joint initiative between the BC Ministry of Education, the BCTF, and Computer Using Educators of BC (CUEBC). CUEBC consists of BCTF member teachers who volunteer their time to serve the members of the Provincial Specialist Association of the British Columbia Teachers’ Federation.
- Project Mapping to ADST 6-9 Competencies, gdoc version
- Intro to CT in the Classroom - specifically “Choose Your Own Adventure” project (pp 53 – 71) in the Unit-1_Unit-2 pdf (gdoc version); how to implement a Choose Your Own Adventure as a (Non-)Fiction, branching story.
- Teacher Training Package
Discover Skills BC
- initiative funded by the BC Government to provide access for secondary students and their teachers and parents to the many educational opportunities available to them in trades and technology training.
CS Unplugged
- CSUnplugged_OS_2015_v3.1.pdf, ELEM INQ GFolder version
- Each Unplugged activity is available on the CS Unplugged to download in PDF format, with full instructions and worksheets.
CS Unplugged is a collection of ~23 free learning activities that teach Computer Science through engaging games and puzzles that use cards, string, crayons and lots of running around. We originally developed this so that young students could dive head-first into computer science, experiencing the kinds of questions and challenges that computer scientists experience, but without having to learn programming first.
Code.org Unplugged Activities
- GFolder
- U1 - Intro to the Art of Computer Science - simple encoding of messages into binary.
- U2 - Computational Thinking - Monster Catalog Face Builder (like Identi-Kit - Google Image search)
- U3 - Graph Paper Programming - drawing pixel images with (simple) instructions.
- U4 - Algorithms - Tangrams.
- U5 - Functions - Beading activity - (Repetitive) Patterns; could be Textiles, or Art.
- U6 - Conditionals: (Coding with Cards) - introduction to “choice/choosing/it this … then that”; iuses playing cards, but any type of game piece oculd be used; highly extensible to “Game Making” in Math / procedures in Science / etc.
- U7 - Song Writing - Cloze-style/”Mad-lib” lyrics (could be used for poetry, as well).
- U8 - Abstraction - Cloze-style/”Mad-lib” mini-story; paragraph level activity, that can connect to “Choose-Your-Own-Adventure+ story-write.
- U9 - Relay Programming - used with U3 - Graph Paper Programming; but done as a Relay Race.
- U10 - The Internet
- code_org-unplugged.md
Creating a Probability Game Based on Story
- Creating a Probability Game (GR4).pdf - curriculum.gov.bc.ca; a cross-curricular way to address probability content in Grade 4 Mathematics and content from Applied Design, Skills and Technologies 4, which is new to the curriculum.
Antartica
- Stanford’s Research in Education & Design (REDlab’s) mission is to conduct research to inform our understanding of design thinking in K-12, undergraduate and graduate educational settings.
- Antarctica Project–Design Thinking version.pdf - The Antarctica Project teaches middle school students to use functions to solve a complex, real-world problem. The unit also includes review of measurement, scale, area, perimeter, and surface area concepts, as well as some computation practice.
Design A Board Game
- Shell Centre for Mathematical Education Publications Ltd. In Design a Board Game, groups carefully design and produce their own board games. These games are then played and evaluated by other class members. This involves developing ideas from 2-dimensional shape-and-space, together with basic concepts of probability. The materials comprise a teacher’s guide, a student booklet, a set of photocopy masters and a set of game boards and cards for the example games.
Programming Cards
- A Different Approach to Teaching Kids and Teens to Code - HackerNoon - Medium.com - the “computer” was the entire classroom with the students being my 1s and 0s. My hope was to have them evaluate Conditions (“If this then do that otherwise do something else”) while understanding the Assumptions I had made, and then importantly — predict Exceptions (when an assumption would fail,) and how we could fix them.
- 10 Ways to teach kids to code - Medium.com
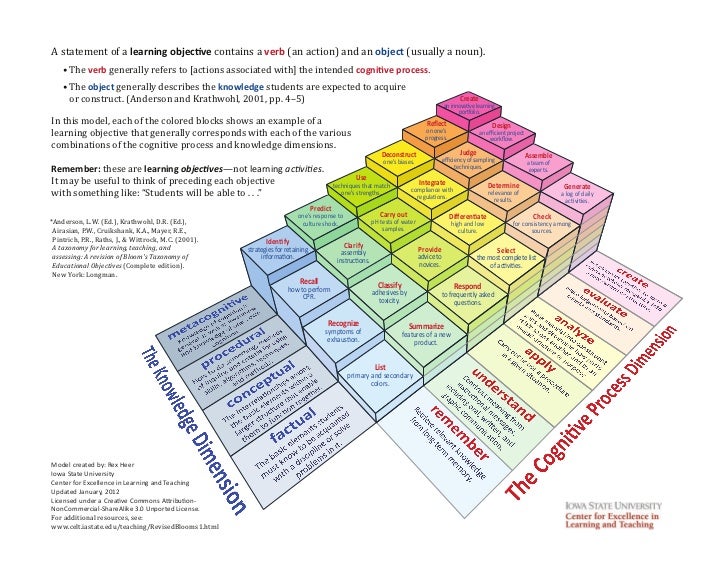
Blooms Revised Taxonomy / Domains of Knowledge
 |
|  — | —
src: http://www.teachthought.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/3d-blooms-c.png | src: https://i.ytimg.com/vi/X2rZoK1pB_8/maxresdefault.jpg
— | —
src: http://www.teachthought.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/3d-blooms-c.png | src: https://i.ytimg.com/vi/X2rZoK1pB_8/maxresdefault.jpg
- bloom-revised-dok - GFolder
- Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy - CELT - ISU Center for Excellence in Learning and Teaching (CELT), Iowa State University (ISU)
- Bloom et al.’s Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain - edpsycinteractive.org
- Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy - Educational Origami
- Applying Webb’s DOK to Blooms Revised Taxonomy
- DOK\/KD Matrix -